Introduction
Portrait photography is a fascinating genre that captures the essence of a person's personality, character, and emotions. Whether it's a professional model, a family member, or a friend, a good portrait photograph can tell a story and create an emotional connection with the viewer. Portrait photography is a genre of photography that aims to capture the personality, character, and emotions of a subject through a photograph.
It can be challenging to create a portrait that truly reflects the subject, but with the right techniques and tips, you can produce a beautiful and memorable image. This article will explore various techniques for portrait photography, including equipment, lighting, composition, posing, expressions, and post-processing. By mastering these skills, you can create portraits that tell a story, connect with the viewer, and evoke emotion.
Here are some techniques and tips for creating beautiful and memorable portrait photographs:
Choose the right equipment: You don't necessarily need a high-end camera or expensive lenses to take great portraits. However, having a camera with manual settings and a lens with a wide aperture (low f-number) can help you achieve a shallow depth of field and create a soft and blurred background that isolates the subject. Additionally, consider using a tripod to keep the camera steady and avoid camera shake.
Choosing the right equipment for portrait photography is crucial in achieving a quality image. While you don't need expensive gear to produce a great portrait, having the appropriate equipment can help you achieve your desired results.
Camera: A camera with manual settings can provide more control over the image. While a DSLR camera is ideal, many mirrorless cameras and even some high-end smartphones offer manual controls as well. The camera's resolution should also be taken into consideration, as higher resolution cameras will allow for more detail in the final image.
Lens: A lens with a wide aperture (low f-number) is ideal for portrait photography as it can create a shallow depth of field, which will blur the background and bring focus to the subject. A 50mm or 85mm prime lens is commonly used for portrait photography as it provides a natural perspective and creates a pleasing depth of field.
Tripod: Using a tripod can help stabilize the camera and prevent camera shake, which can result in a blurry image. A tripod is especially useful when using slower shutter speeds or when taking multiple shots of the same subject.
Remote Shutter Release: A remote shutter release or cable release can be used to prevent camera shake when pressing the shutter button on the camera. It's especially useful when using a tripod and can help create a sharp and crisp image.
Light Meter: A light meter can help you measure the light in a scene, which can assist in setting the proper exposure for the image.
[caption id="attachment_192482" align="alignnone" width="1500"]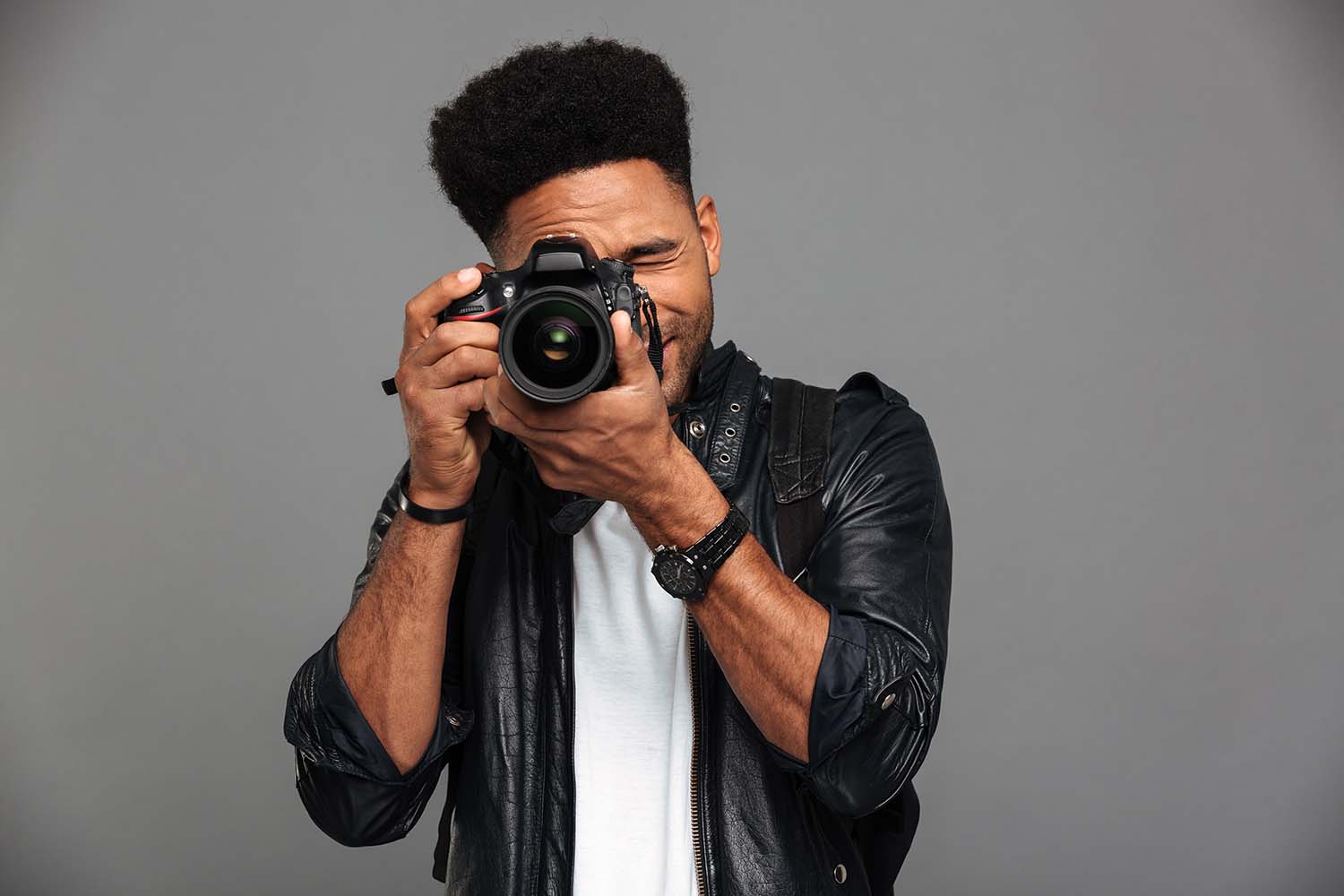 Portrait Photography[/caption]
Portrait Photography[/caption]
Also Read This: Becoming Recognized on EyeEm: Strategies for Success
Lighting
Lighting is one of the most critical elements in portrait photography. Use natural light whenever possible, positioning your subject near a window or outside during golden hour (an hour before sunset or after sunrise) for soft and warm light. Alternatively, you can use artificial light sources such as studio strobes, soft boxes, or reflectors to create different lighting effects and shapes on the face.
Lighting is a crucial element in portrait photography, as it can dramatically affect the mood and feel of the image. Here are some lighting techniques to consider when capturing a portrait:
Natural light: Natural light can create beautiful and flattering portraits when used correctly. Look for soft, diffused light, such as during the early morning or late afternoon, to avoid harsh shadows and highlights. You can also use reflectors to bounce light back onto the subject, providing additional illumination and enhancing their features.
Studio lighting: Studio lighting provides more control over the light and can be used to create a variety of different looks and styles. Use softboxes or umbrellas to diffuse the light and create a soft and even illumination across the subject's face. Place the lights at different angles and distances to create different effects, such as Rembrandt lighting, where the light is placed above and to the side of the subject's face, creating a triangle of light under the eye.
Window lighting: Window lighting can be used as a natural and flattering light source for portraits. Place your subject near a window with diffused light to create a soft and gentle illumination. You can also use curtains or blinds to control the amount of light and create different patterns and shapes on the subject's face.
Backlighting: Backlighting can create a dramatic and striking portrait, with the subject appearing to glow from within. Position your subject in front of a light source, such as the sun or a lamp, and shoot towards the light to create a backlit effect. This technique can be challenging to master, but the results can be stunning.
[caption id="attachment_192483" align="alignnone" width="1500"]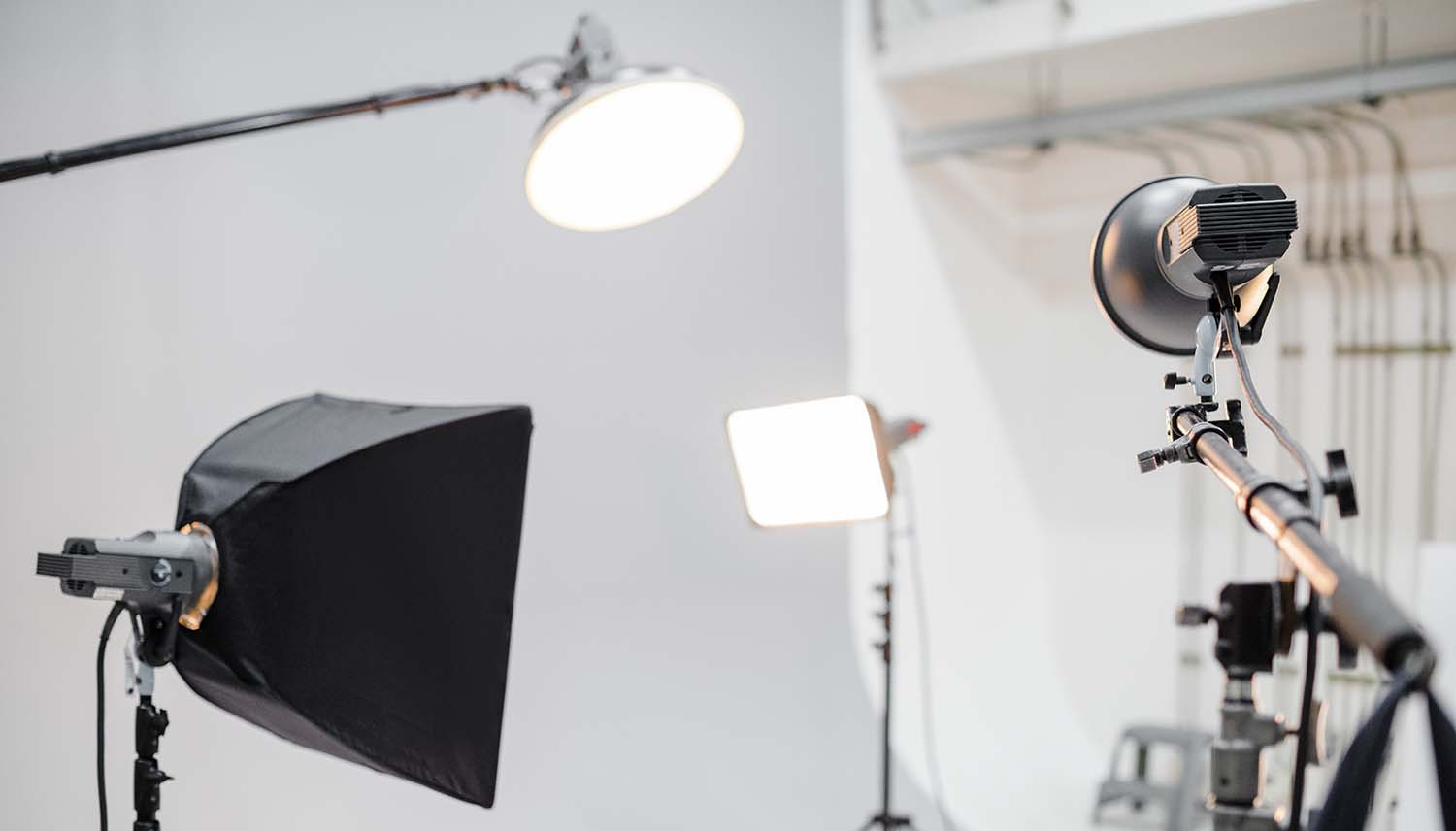 Lighting[/caption]
Lighting[/caption]
Also Read This: Boosting Sales on Picfair: Strategies for Success
Composition
The composition of your portrait can also make a difference in the final result. Consider the rule of thirds, where you divide the frame into thirds vertically and horizontally and place the subject's eyes on one of the intersections. Composition is the arrangement of elements within a photograph and is an important aspect of creating a successful portrait. Here are some composition techniques to consider when capturing a portrait:
Rule of thirds: The rule of thirds is a composition technique that involves dividing the image into thirds both horizontally and vertically, creating a grid of nine squares. Place the subject's eyes on one of the intersections of the grid to create a visually pleasing and balanced image.
Framing: Framing involves using elements within the photograph to create a frame around the subject, drawing the viewer's attention towards the subject. For example, you can use a doorway or window to frame the subject, creating a sense of depth and dimension within the image.
Leading lines: Leading lines are lines within the photograph that guide the viewer's eye towards the subject. Use elements such as a pathway, a fence, or a row of trees to create leading lines that lead towards the subject.
Symmetry: Symmetry involves creating a balanced and mirrored image by placing the subject in the center of the frame. This technique can create a sense of calm and harmony within the image.
Depth of field: Depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in the photograph that appear sharp. Use a shallow depth of field to create a blurred background, drawing the viewer's attention towards the subject.
[caption id="attachment_192484" align="alignnone" width="1500"]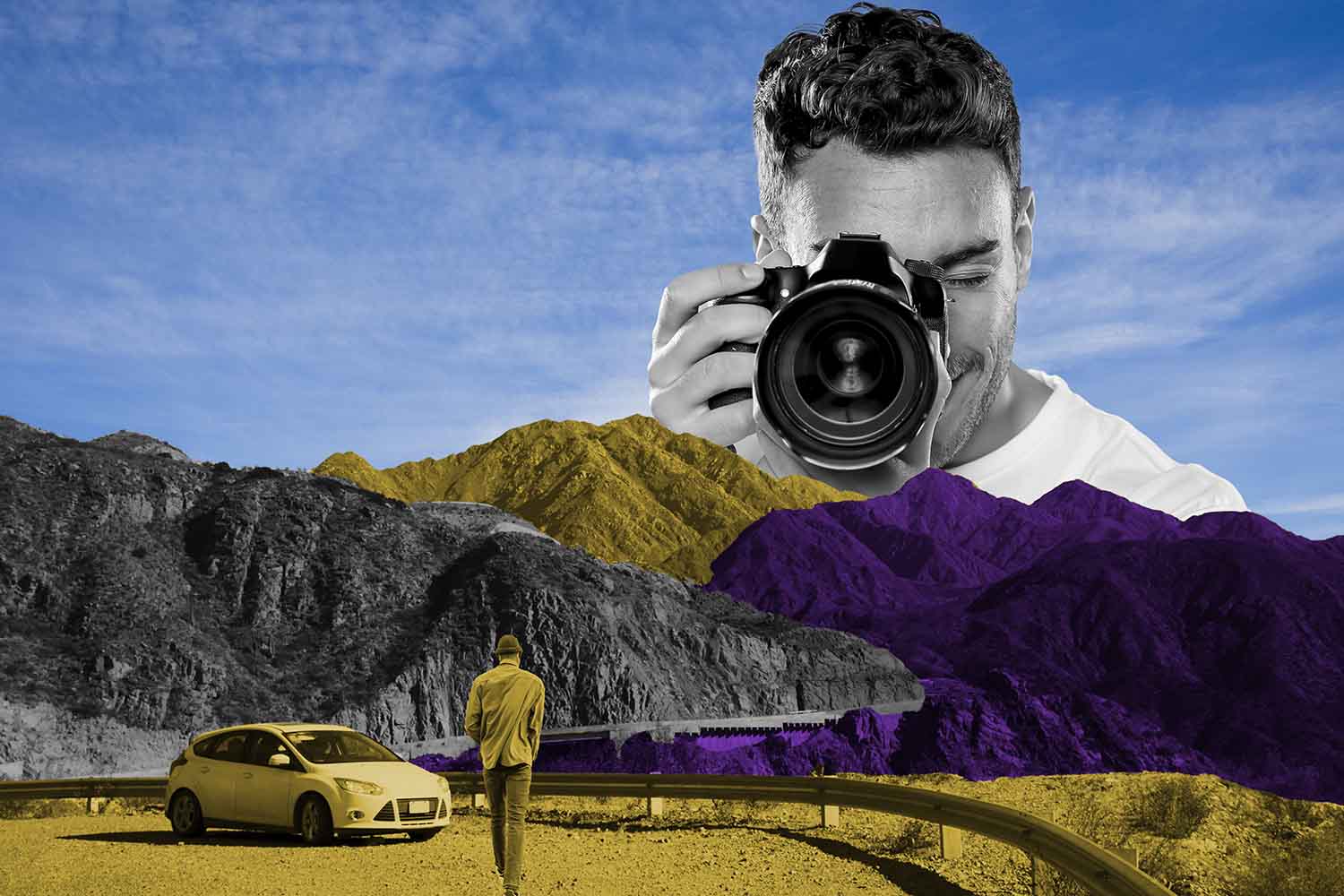 Composition[/caption]
Composition[/caption]
Also Read This: Unlocking Creative Power: Navigating Adobe Stock Subscription Costs
Posing
Posing your subject can be tricky, but it's essential to create a flattering and natural-looking portrait. Communicate with your subject and give them direction on how to position their body and face. Avoid stiff and unnatural poses and encourage your subject to relax and be themselves.
Posing is a crucial element of portrait photography, as it can convey emotions, personality, and relationships between subjects. Here are some posing techniques to consider when capturing a portrait:
Body language: Body language can communicate emotions and personality in a portrait. Use cues such as tilting the head, crossing the arms, or leaning forward to convey a specific mood or feeling.
Eye contact: Eye contact can create a connection between the subject and the viewer. Encourage the subject to look directly at the camera or have them look at something just off-camera to create a more natural and relaxed pose.
Group posing: When capturing a group portrait, consider the relationship between the subjects and their relative sizes. Position taller subjects in the back and use different levels, such as sitting or standing, to create a sense of depth within the image.
Hands and feet: Hands and feet can often be overlooked in a portrait, but they can convey important elements such as confidence or nervousness. Encourage the subject to pose with their hands in a natural position or to cross their feet at the ankles to create a relaxed and comfortable pose.
Props: Props can be used to create a sense of context and add interest to the portrait. Use items such as a musical instrument, a book, or a flower to provide additional information about the subject and create a visually interesting composition.
[caption id="attachment_192485" align="alignnone" width="1500"] Posing[/caption]
Posing[/caption]
Also Read This: A Closer Look at Celebrity Events Covered by WireImage
Expressions
Capturing a genuine and authentic expression is crucial in portrait photography. Encourage your subject to show different emotions and moods, such as happiness, sadness, or contemplation. Also, pay attention to the eyes, which are often the focal point of a portrait. Make sure they are in focus, and the subject's gaze is directed towards the camera or a specific point.
Expressions are a key element of portrait photography as they convey the subject's emotions and personality. Here are some tips for capturing authentic expressions in your portraits:
Establish a connection: Create a comfortable and relaxed environment for the subject to establish a connection with them. This can help them feel more at ease and open up, resulting in more natural and authentic expressions.
Encourage movement: Movement can help create a natural and candid expression. Encourage the subject to move around, change positions, or interact with their surroundings to create a more relaxed and spontaneous expression.
Provide direction to the subject to help them achieve the desired expression. Use verbal cues, such as "smile" or "laugh," or physical cues, such as asking them to look in a specific direction or tilt their head.
The eyes are a crucial element in capturing an authentic expression. Encourage the subject to look directly at the camera or to focus on something off-camera to create a more natural and engaging expression.
Capturing an authentic expression may take time and patience. Don't rush the process and take the time to establish a connection with the subject and create a comfortable environment.
[caption id="attachment_192486" align="alignnone" width="1500"] Expressions[/caption]
Expressions[/caption]
Also Read This: Instagram Fusion: Link Shopify to Instagram Impact
Post-processing
Editing your photos can enhance their visual impact and create a consistent look and feel. Use editing software such as Adobe Lightroom or Photoshop to adjust the exposure, contrast, and color balance. Additionally, consider applying a selective focus effect, black and white conversion, or skin retouching if necessary.
Post-processing is an important step in portrait photography that can enhance the final image. Here are some post-processing techniques to consider:
Cropping: Cropping can help improve the composition of the image by removing distracting elements or adjusting the placement of the subject within the frame.
Color correction: Adjusting the colors can help improve the overall tone and mood of the image. This can involve adjusting the temperature, tint, saturation, and contrast of the image.
"Photography is a way of feeling, of touching, of loving. What you have caught on film is captured forever... It remembers little things, long after you have forgotten everything." - Aaron Siskind
Retouching: Retouching can help remove blemishes or imperfections from the subject's skin or clothing. Use tools such as the clone stamp or healing brush to remove unwanted elements.
Sharpening: Sharpening can help improve the overall clarity of the image. Use tools such as the sharpening filter or unsharp mask to sharpen the details in the image.
Effects: Applying creative effects such as black and white conversion or adding a vignette can add visual interest to the image and help convey a specific mood or emotion.
When post-processing portraits, it is important to maintain a natural and authentic look. Avoid over-processing the image and focus on enhancing the elements that already exist in the image. Presenting a video filled with fantastic tips for portrait photography.
Also Read This: 5 Tips for Boosting Your Facebook Reach and Engagement
Pros & Cons
Pros
- Portrait photography allows for creative expression and experimentation with lighting, composition, and posing.
- Building a connection with subjects can lead to meaningful and authentic portraits that capture their personality and emotions.
- Portrait photography can be a lucrative business, with opportunities for weddings, family portraits, and professional headshots.
- Capturing a beautiful and emotionally impactful portrait can be personally satisfying and rewarding.
Cons
- Portrait photography requires technical knowledge of equipment, lighting, and composition, which can be challenging to master.
- The process of setting up the shot, working with the subject, and post-processing can be time-consuming, especially for complex portraits.
- High-quality equipment can be expensive, making it difficult for photographers to invest in the necessary gear.
- Portrait photography can be limiting in terms of creative freedom, especially for commercial shoots where the client may have specific requirements or preferences.
Also Read This: Visual Treasure Hunt: Free Downloads from Getty Images
Conclusion
Portrait photography is a popular and rewarding pursuit that requires a combination of technical knowledge, creativity, and people skills. By choosing the right equipment, lighting, composition, posing, and post-processing techniques, photographers can capture authentic and emotionally impactful portraits that connect with viewers. However, there are potential challenges and limitations, including technical difficulties, time constraints, and creative limitations. By understanding the potential pros and cons, photographers can navigate these challenges and make informed decisions about their approach to the craft. Overall, portrait photography offers a unique opportunity to capture the essence of an individual and create meaningful and lasting images.
FAQ
What is portrait photography?
Portrait photography is a type of photography that involves capturing images of individuals, typically in a posed or staged setting. The goal of portrait photography is to capture the subject's personality, emotions, and physical appearance.
What equipment do I need for portrait photography?
You will need a camera, preferably a DSLR or mirrorless camera, along with lenses suitable for portrait photography. A 50mm or 85mm prime lens is a popular choice. You will also need lighting equipment, such as a flash or continuous lighting, and a backdrop or setting suitable for portraits.
What is the best lighting for portrait photography?
The best lighting for portrait photography depends on the look you are trying to achieve. Natural light can be flattering and create a soft and natural look, while artificial lighting can be more controllable and consistent. A combination of both natural and artificial light can create a dynamic and visually interesting portrait.
How do I pose my subjects for portrait photography?
Posing your subjects for portrait photography involves creating a comfortable and relaxed environment for them to be themselves. Encourage natural movements and expressions, and use verbal and physical cues to direct their posture and expression.
How do I edit my portraits in post-processing?
Editing your portraits in post-processing involves adjusting elements such as color, contrast, and sharpness. You can also retouch the image to remove blemishes or imperfections. It's important to maintain a natural and authentic look and avoid over-processing the image.